Our novel agent, the empty SV40 capsid, is composed of a single protein and does not contain any genetic material. This natural agent responds to a wide array of malfunctions in the organism.
Wild type SV40 was declared by the NIH to be “non-pathogenic to human individuals” (https://osp.od.nih.gov/wp-content/uploads/NIH_Guidelines.pdf). All the more so for the empty capsids, which do not contain any genetic material and cannot propagate.
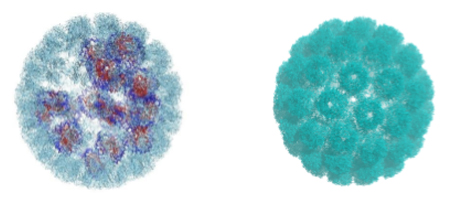
Below is a high resolution, molecular model of the wild type virus and the empty capsid, solved by our group based on small angle X-ray scattering.
Wild Type SV 40 Empty capsid (NC)
The NC treatment is a paradigm shift at several levels for the treatment of diseases with complex pathology:
- The NCs modulate gene expression profile of the host leading to activation of numerous pathways that promote tissue repair and recovery.
- The NCs affect different genes in different diseases, responding to the respective pathophysiology.
- The NCs induce broad host anti-microbial defense mechanisms, unlike antibiotics that directly kill pathogens and contribute to the rise of drug resistant bacteria.
- The elicited signaling pathways become modified with time, adjusting to the recovery process of the treated animals.
- The NCs have a negligible effect on healthy animals, suggesting negligible side effects in clinical applications.
These properties taken together indicate that the NCs bring the sick body to homeostasis – a balance of its physical, chemical and biological state.
In different experiments using animal models we show that:
- The survival of rats inflicted with severe sepsis and pre-treated with NCs is 75%, while all the rats that received placebo died within 4 days (Ben-Nun-shaul et al, 2020, Oncotarget 11:574-588).
- Pre-treatment with NCs increased survival of animals with acute kidney injury (AKI) induced by mercury poisoning (Butin-Israeli et al, PLoS ONE Aug 20;3(8):e2998)_and by the cancer drug cis-platinum (unpublished).
- In rats inflicted with traumatic brain injury (TBI), post treatment with NCs improved brain function, suggesting that pre-treatment is not an inherent requirement of NC therapy (unpublished).
Application
- Sepsis – current focus – data obtained from studies in a rat model (Ben-Nun-shaul et al, 2020, Oncotarget 11:574-588).
- Acute kidney injury (AKI) – efficacy demonstrated in two mouse models: (mercury-induced AKI (Butin-Israeli et al, 2008, PLoS One Aug 20;3(8):e2998) and cis-platin induced AKI (unpublished).
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI) – preliminary study demonstrated recovery of brain damage in mice (unpublished).
